
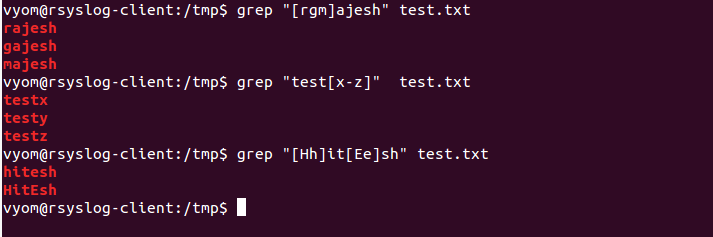
In addition to automatic filtering, ripgrep also provides more manual or ad. Were syntax errors in the pattern, inaccessible input files, or other system errors. Unlike GNU grep, ripgrep stays fast while 119: Is it really faster than. (The -v option inverts the sense of the exit status.) Exit status is 2 if there Grep searches the input files (standard input default) for lines that match the pattern, a regular expression as defined in regexp(7) with. Normally, exit status is 0 if matches were found, and 1 if no matches were found. It could have 0, 1 or more than 1 matches. on the other hand doesnt require a match. The backreference \n, where n is a single digit, matches the substring previously matched by the nth parenthesized subexpression of the regular expression. +requires that the pattern before it would have at least one match and can also have more. Repetition takes precedence over concatenation, which in turn takes precedence over alternation.Ī whole subex-pression may be enclosed in parentheses to override these precedence rules. Two regular expressions may be joined by the infix operator | the resulting regular expression matches any string matching either subexpression. Two regular expressions may be concatenated the resulting regular expression matches any string formed by concatenating two substrings that respectively match theĬoncatenated subexpressions. This manual is for grep, a pattern matching engine. This manual is for version 3.7 of GNU Grep. matched (non-empty) parts of a matching line means non empty line right Update. Word, and \B matches the empty string providedĪ regular expression may be followed by one grep prints lines that contain a match for one or more patterns. grep manual quote:-o, -only-matching Print only the matched (non-empty) parts of a matching line, with each such part on a separate output line. Matches the empty string at the edge of a Respectively match the empty string at theīeginning and end of a word. Metacharacters that respectively match theĮmpty string at the beginning and end of a Include a literal ] place it first in the Of the symbolic names, and must be included The brackets in these class names are part

For example, ] meansĭependent upon the ASCII character encoding, Their names are self explanatory,Īnd they are, , , A range of ASCII characters may beĬharacters, separated by a hyphen. If the first character of the list is theĬaret ^ then it matches any character notĮxpression matches any singleĭigit. Matches any single character in that list Switch causes grep to report byte offsetsĪs if the file were Unix-style text file, To the matching mechanism verbatim if the For a regular expression pattern, this is like parenthesizing the pattern and then surrounding it with and. x, -line-regexp Select only those matches that exactly match the whole line. Strips the CR characters from the originalįile contents (to make regular expressions grep -inx -d skip 'favicon.ico' test.txt:1:favicon.ico. Under MS-DOS and MS-Windows, grep guesses Fgrep is theĪll variants of grep understand the following En la versión de grep de GNU, no hay diferencia en usar una u otra en cuanto a la funcionalidad disponible. Not identical) to grep -E, and is compatible El programa grep entiende dos versiones diferentes de sintaxis para las expresiones regulares: la básica y la extendida. In addition, two variant programs egrep andįgrep are available. By default, grep prints the matching lines. GREP command can be used to find or search a regular expression or a string in a text file.Grep searches the named input files (or standard input if no files are named, or the file name - is given)įor lines containing a match to the given pattern. GREP will by default display any lines in a file that contain the expression. The basic usage of the command is grep expression filename. GREP stands for Globally Search a Regular Expression and Print. Example: “” will match all lines that contain a vowel.Example: “$*” will match the lines that contain the string “$*”.Example: “^Name” matches all lines that start with the string “Name”.How use grep command in Unix with example? When it finds a match, it prints the line with the result. The text search pattern is called a regular expression. Grep is a Linux / Unix command-line tool used to search for a string of characters in a specified file. Grep is an acronym that stands for Global Regular Expression Print.



 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
